Reshaping the future of the Earth requires a hefty investment. Recent years, the financial world has witnessed the emergence of an innovative financing mechanism known as green bonds.
These bonds represent not just an investment in financial returns but also in the health and future of our planet. As investors increasingly seek opportunities that align with their ethical and environmental values, green bonds have surged in popularity, offering a pathway to contribute to sustainable initiatives while securing potential financial gains.
What are green bonds?
Green bonds are a category of fixed-income securities designed to fund projects that have positive environmental and climate benefits. Their primary objective is to raise capital for clean transportation, renewable energy, energy efficiency, and other sustainable projects. These bonds are similar to traditional bonds in their structure but are distinguished by their explicit commitment to environmental sustainability.

A little background…
The inception of the green bond market can be traced back to the pioneering efforts of the World Bank, which issued the first recognized green bond in 2008. This marked the beginning of a new era in capital markets, where the mobilization of funds for environmental projects became a focal point. Since then, the market has expanded rapidly, with a diverse range of bond issuers including governments, corporations, and financial institutions stepping forward to support green initiatives.
Issuing a green bond involves a complex process, where projects are carefully selected based on their environmental benefits. The Green Bond principles ensure that the funds raised are exclusively used to finance or refinance projects that contribute to environmental sustainability.
So, what are the types of green bonds?
Within the rise of green bond market, a diverse array of entities have emerged as issuers, each playing a pivotal role in the expansion and depth of this financial instrument. These issuers can be broadly categorized into three main groups:
- Governments: National and local governments issue green bonds as a strategic approach to fund public environmental projects, such as sustainable infrastructure, water management, and pollution control.
- Corporations: Corporate green bonds are issued by companies aiming to finance green projects within their operations or supply chains. These might include initiatives to improve energy efficiency, reduce carbon footprints, or develop sustainable resources. By issuing green bonds, corporations not only gain access to capital to fund these projects but also demonstrate their commitment to sustainable business practices to investors and stakeholders.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and other financial institutions issue green bonds to raise funds for lending to environmentally sustainable projects. This category includes green bonds that finance projects in renewable energy, green buildings, and other areas contributing to environmental sustainability.
The purpose of green bonds
Green bonds serve a transformative purpose in the global effort to address environmental challenges and promote sustainability. These financial instruments are specifically designed to raise capital for projects with positive environmental impacts, providing a tangible way for investors to contribute to sustainable development goals.
The spectrum of projects financed by green bonds is broad, encompassing a range of sectors like renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable land use, clean transportation, water management, and waste management.
For instance, Starbucks, a global coffee roaster and a significant player in the coffee supply chain, has leveraged their green bonds to finance a range of sustainability projects. These initiatives include purchasing beans from farmers practicing its Coffee and Farmer Equity (C.A.F.E) standards, supporting farmer support centers, and providing smallholder loans through the company’s global farmer fund. This approach not only advances Starbucks’ sustainability agenda but also contributes to protecting coffee suppliers against various risks, including environmental risks like water inefficiency, soil degradation, and deforestation.
Similarly, PepsiCo’s engagement in green bond issuance underscores the potential of these instruments in driving sustainable agricultural practices. The company raised $1.25 billion through its green bond offering, with a significant portion of the proceeds directed towards agricultural and value chain-focused sustainability initiatives. These initiatives encompass a wide range of projects, from regenerative agriculture and water sustainability to circular economy efforts and decarbonization of supply chains. By focusing on areas such as reducing fertilizer use, enhancing water efficiency, and investing in renewable energy for the supply chain, PepsiCo’s green bond initiatives exemplify how these financial tools can support comprehensive sustainability goals in agriculture.
How green bonds work
Green bonds operate within the framework of traditional bond markets but are distinguished by their explicit focus on financing projects with environmental benefits. The process from issuance to investment reflects a commitment to sustainability at every step, ensuring that the funds raised contribute effectively to environmental goals. Here’s a closer look at how green bonds work:
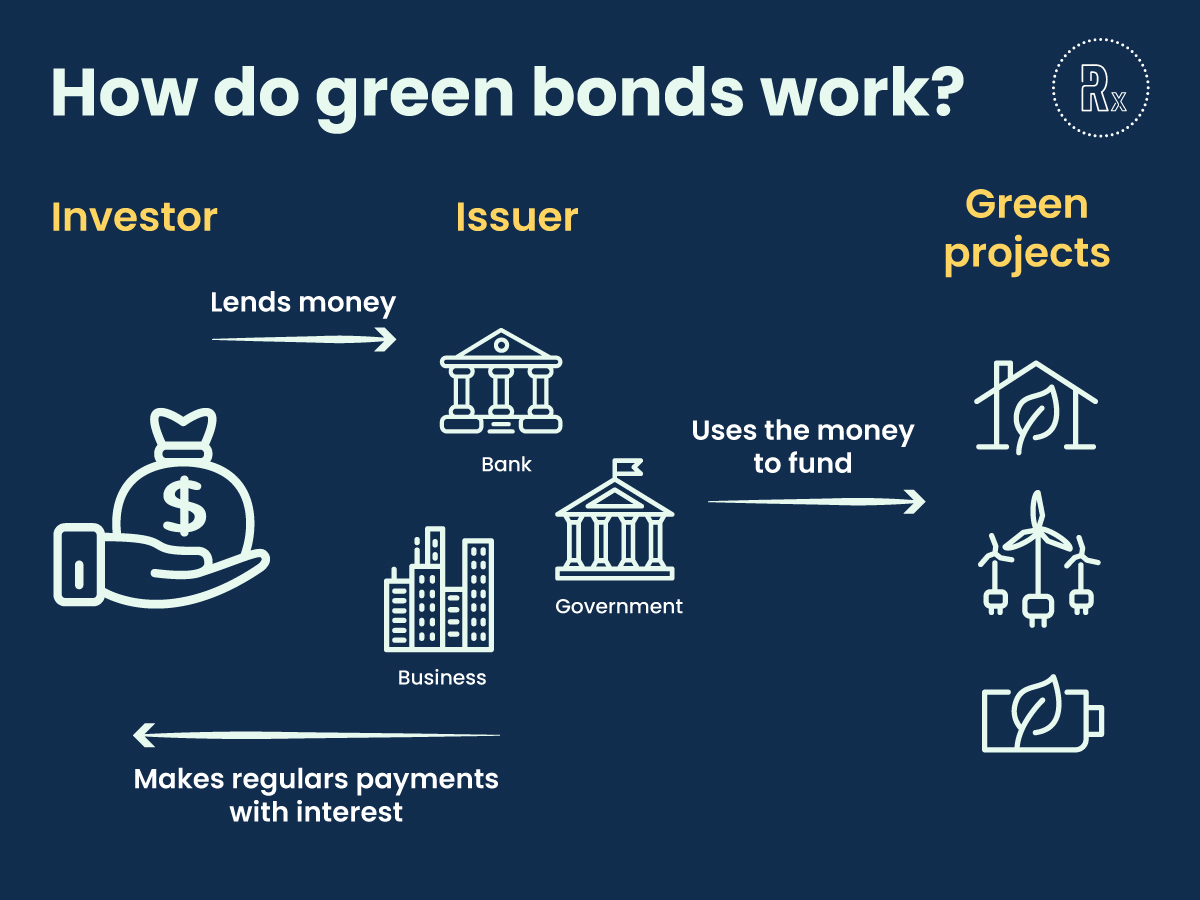
1. Issuance and Certification:
- Green bonds are issued by entities ranging from governments and corporations to financial institutions, all of whom are looking to fund environmentally sustainable projects. The issuance process involves defining the bond’s terms, including its purpose, tenure, and interest rates.
- Certification plays a crucial role in ensuring the green credentials of the bonds. Various standards and frameworks, such as the Green Bond Principles and the Climate Bonds Standard, provide guidelines on transparency, reporting, and project selection. These standards help investors assess the environmental impact of their investments.
2. Project selection and verification:
- The proceeds from green bonds are earmarked for projects that have clear environmental benefits, such as renewable energy installations, energy efficiency upgrades, sustainable water management, and more. The selection of projects is guided by the issuer’s environmental objectives and the standards set by the green bond framework.
- Third-party verifiers play a critical role in the green bond market by providing independent assurance that the bonds’ proceeds are allocated to truly green projects. This verification process adds a layer of credibility and trust, ensuring that the projects funded align with the bond’s environmental objectives.
3. Funding and implementation:
- Once issued, green bonds attract investment from a diverse pool of investors who are interested in combining financial returns with environmental impact. The funds raised are then allocated to the selected green projects.
- The implementation of these projects involves not just the utilization of the funds but also the adherence to sustainable practices throughout the project’s lifecycle, from planning and construction to operation.
4. Reporting and transparency:
- Regular reporting on the use of proceeds and the environmental impact of the funded projects is a key aspect of green bonds. Issuers provide detailed updates on the progress of the projects, their environmental benefits, and how the funds are being used.
- This transparency helps maintain investor confidence and ensures accountability, reinforcing the bonds’ green credentials and the issuer’s commitment to sustainability.
5. Market development:
- The green bond market has seen significant growth, with an increasing number of issuers and investors participating. This growth is supported by the development of new standards, increasing investor demand for sustainable investment options, and a broader recognition of the role of finance in addressing environmental challenges.
Invest in our planet: The green bond imperative
It’s evident that these financial instruments are not just an investment in the future of our planet, but also a testament to the power of innovative financing in driving environmental sustainability. Green bonds offer a bridge between the financial world and the urgent need for action on climate change, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution.



